Future integrated communication network architectures enabling heterogeneous service provision
This paper summarizes expectations and requirements towards future converged communication systems denoted by 5th Generation (5G). Multiple research and standardization activities globally contribute to the definition and specification of an Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to provide business customers and residential users with both, existing and future upcoming services which demand for higher data rates and granted performance figures in terms of QoS parameters, such as low latency and high reliability. Representative use case families are threefold and represented as enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), massive Internet of Things (mIoT), and Critical Communication, i.e. Ultra-Low Latency (ULL)/Ultra-High Reliability (UHR). To deploy and operate a dedicated network for each service or use case separately would raise the expenses and service costs to an unduly high amount. Instead provision of a commonly shared physical infrastructure offering resources for transport, processing, and storage of data to several separated logical networks (slices) individually managed and configured by potentially multiple service providers is the main concept of this new approach.
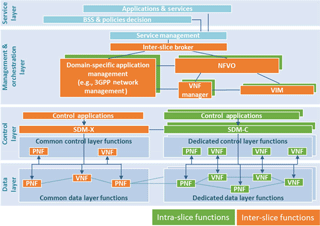
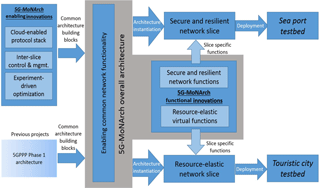
Beside a multitude of other initiatives the EU-funded 5G NORMA project (5G Novel Radio Multiservice adaptive network Architecture) has developed an architecture which enables not only network programmability (configurability in software), but also network slicing and Multi Tenancy (allowing independent 3rd parties to offer an end-to-end service tailored according to their needs) in a mobile network. Major aspects dealt with here are the selectable support of mobility (on-demand) and service-aware QoE/QoS (Quality of Experience/Service) control.
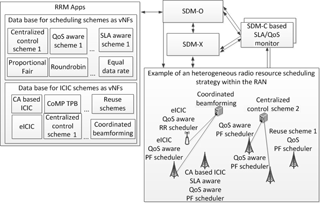
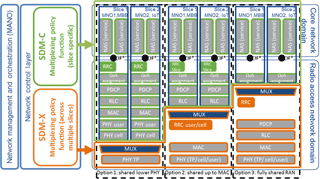
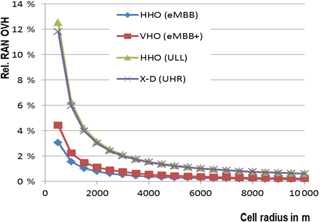
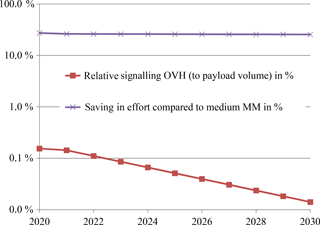
Specifically we will report on the outcome of the analysis of design criteria for Mobility Management schemes and the result of an exemplary application of the modular mobility function to scenarios with variable service requirements (e.g. high-terminal speed vs. on-demand mobility or portability of devices). An efficient sharing of scarce frequency resources in new radio systems demands for tight coordination of orchestration and assignment (scheduling) of resources for the different network slices as per capacity and priority (QoS) demand. Dynamicity aspects in changing algorithms and schemes to manage, configure, and optimize the resources at the radio base stations according to slice specific Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are investigated. It has been shown that architectural issues in terms of hierarchy (centralized vs. distributed) and layering, i.e. separation of control (signaling) and (user) data plane will play an essential role to increase the elasticity of network infrastructures which is in focus of applying SDN (Software Defined Networking) and NFV (Network Function Virtualization) to next generation communication systems.
An outlook towards follow-on standardization and open research questions within different SDOs (Standards Defining Organizations) and recently started cooperative projects concludes the contribution.